At Nunyarra Dental, we believe that knowledge is the first step in maintaining healthy teeth and the best oral hygiene routine. In a previous article, we discussed “How do I practice good oral hygiene at home?“. Continuing on that theme, this blog post is dedicated to shedding light on a common oral health issue – gum disease. Understanding what it is, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments can significantly enhance your dental health.
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a prevalent issue affecting many Australians. It begins as gingivitis—an inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup at the gumline due to inadequate dental hygiene. If not addressed promptly, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, leading to potential tooth loss and other health issues.
Here are the common types of gum diseases:
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease. It occurs due to plaque buildup at the gum line caused by poor oral hygiene. Gingivitis is usually associated with red, swollen gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Bad breath may also be a sign. The good news is that this condition is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. This severe form of gum disease affects the bones supporting the teeth. In addition to the symptoms of gingivitis, signs of periodontitis can include receding gums, formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums, loose or shifting teeth, changes in how teeth fit together upon biting down, or even tooth loss. Periodontitis requires immediate professional treatment to prevent further complications.
- Aggressive Periodontitis: This type of gum disease occurs in patients who are otherwise healthy and usually begins in childhood or young adulthood. It is characterised by rapid bone destruction and attachment loss, often familial.
- Chronic Periodontitis: This is the most common form of periodontitis and is characterised by the slow progression of gum detachment. It occurs mainly in adults but can occur at any age.
- Necrotizing Periodontal Disease: This gum disease is characterised by the death (or necrosis) of gum tissue, tooth ligaments, and supporting bone caused by lack of blood supply (ischemia), resulting in severe infection. It’s often seen in individuals with a severely compromised immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or certain types of cancer.
Professional dental examinations are the most reliable way to identify gum disease. Dentists or periodontists (specialists in gum disease) can assess your oral health and identify any signs of gum disease.
Maintaining regular dental check-ups and practising good oral hygiene to prevent gum disease is essential. This includes brushing your teeth twice daily, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Causes and Symptoms of Gum Disease

The primary cause of gum disease is a buildup of bacterial plaque, a sticky, colourless film that forms on your teeth. If not removed by daily brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, contributing to infection in the gum tissues. We have covered more about this in our article “Why Dental Checkups & Scale & Cleaning Are Important“.
Other factors can also increase the risk of gum disease, such as smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes in women, certain medications, genetic predisposition, and stress. Understanding “What causes tooth pain“ can further assist in spotting potential dental problems early.
The symptoms of gum disease often go unnoticed in the early stages as it’s typically painless. However, redness, swollen or tender gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose or shifting teeth, and changes in your bite are signs to look out for.
Treatments for Gum Disease
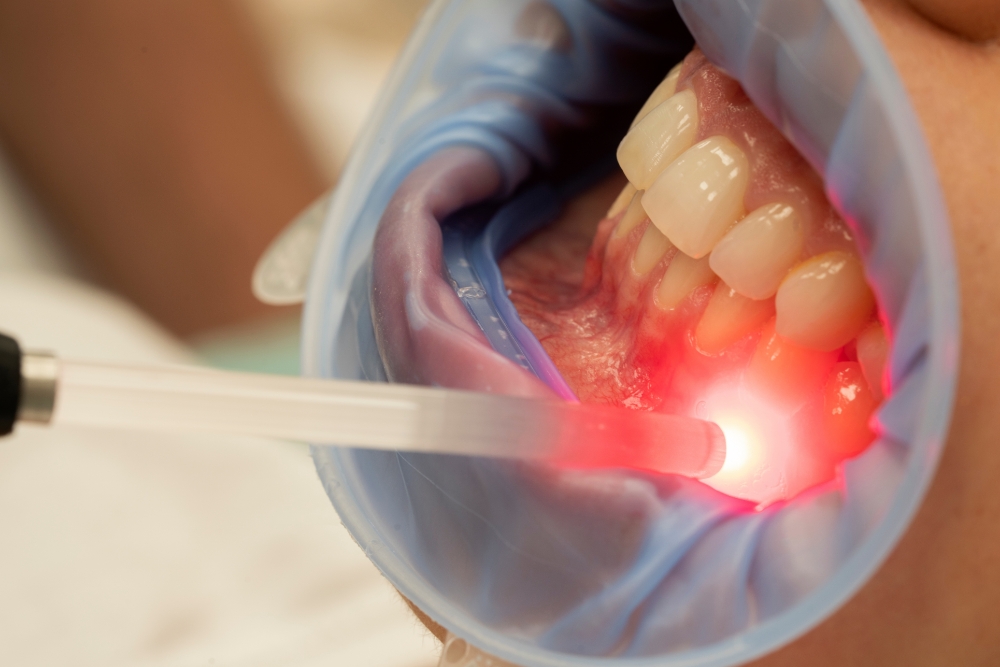
There are several treatment options for gum disease, depending on its severity:
- Professional Dental Cleaning: As part of your regular checkup, we perform a professional cleaning that includes plaque and tartar removal, helping prevent or halt the progress of gum disease.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This is a deep-cleaning, non-surgical procedure recommended when gum disease progresses beyond its earliest stage. The process involves removing plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and below the gum line while root planing smoothes the tooth root, helping the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Flap Surgery/Pocket Reduction Surgery: This surgical procedure might be necessary in more severe cases. The surgery involves lifting back the gums, removing tartar, and then securing the gums back into place to fit snugly around the tooth.
- Tissue and Bone Grafts: If the bone or tissue supporting the teeth is damaged due to severe gum disease, we may recommend grafts. This procedure involves replacing the damaged bone or tissue, encouraging your body to regenerate these structures.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This surgical procedure is recommended when the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed due to severe gum disease. A mesh-like fabric is inserted between the bone and gum tissue, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow.
Dental issues can sometimes become emergencies. In such situations, please refer to our post on “What To Do If You Have A Dental Emergency“, and don’t hesitate to contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions
To help you better understand gum disease, we’ve compiled some frequently asked questions:
- Can gum disease lead to other health problems?
Yes, research suggests a link between gum disease and other health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s. - Is gum disease reversible?
Early stages of gum disease (gingivitis) are reversible with good oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings. Advanced gum disease (periodontitis) can be managed but not entirely reversed. - How often should I visit the dentist to prevent gum disease?
You should have a dental check-up at least twice a year. Depending on your oral health, your dentist might recommend more frequent visits. - Can children get gum disease?
Yes, children can get a mild form of gum disease called gingivitis. Good oral hygiene practices can help prevent this. - What should I do if I think I have gum disease?
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gum disease, schedule an appointment at Nunyarra Dental. Our team can evaluate your symptoms and provide the best treatment plan for you.
At Nunyarra Dental, we’re dedicated to helping our patients achieve and maintain healthy smiles. Schedule an appointment with us today to ensure your smile is at its healthiest.

